Content

Balance SheetA balance sheet is one of the financial statements of a company that presents the shareholders’ equity, liabilities, and assets of the company at a specific point in time. It is based on the accounting equation that states that the sum of the total liabilities and the owner’s capital equals the total assets of the company. Noncurrent assets include a variety of assets, such as fixed assets and intellectual property, and other intangibles.
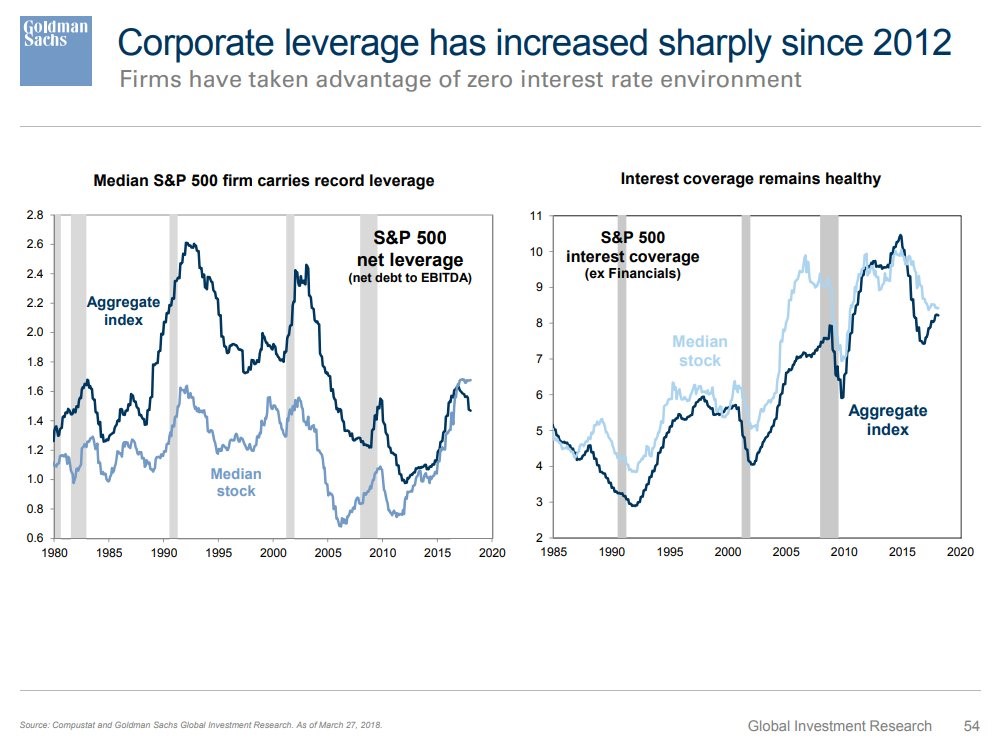
Examples of tangible assets include land, buildings, equipment, machinery, furniture, and natural resources such as mineral and petroleum resources. Production facilities used by automakers, for instance, would be classified as noncurrent assets. Growing cash reserves often signal strong company performance; dwindling cash can indicate potential difficulties in paying its debt . However, if large cash https://online-accounting.net/ figures are typical of a company’s balance sheet over time, it could be a red flag that management is too shortsighted to know what to do with the money. Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) are long-term assets vital to business operations and not easily converted into cash. Noncurrent assets are depreciated in order to spread the cost of the asset over the time that it is used; its useful life.
Is contributed capital a non-current asset or a current asset? Does it have a debit or credit…
Investors make capital contributions when a company issues equity shares based on a price that shareholders are willing to pay for them. The total amount of contributed capital or paid-in-capital represents their stake or ownership in the company. Firm N has a current ratio of 2.5 and current assets of $157,500. In the case of retained earnings, there is no capital contribution by the investors and hence do not form as the part of the contributed capital of the company.
- Now that we know what the purpose of this financial statement is, let’s analyze how this report is formatted in a little more detail.
- Paid-in capital is the capital paid in by investors during common or preferred stock issuances.
- A picture is provided of each future economic benefit owned or controlled by the company as well as its debts .
- Amount of liability, recognized in statement of financial position, for defined benefit pension and other postretirement plans, classified as noncurrent.
- Liabilities expected to be settled or paid within one year or one operating cycle of the business, whichever is greater, are classified as current liabilities.
Accounts receivable are the amounts billed to your customers and owed to you on the balance sheet’s date. You should label all other accounts receivable appropriately and show them apart from the accounts receivable arising in the course of trade. If these other amounts are currently collectible, they may be classified as current assets. The short-term debt of an organization may be settled with cash and equivalents . The predicted payments from clients that will be collected within a year make up accounts receivable.
What Are Examples of Current Assets and Noncurrent Assets?
Cash includes currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Generally, only investments with original maturities of three months or less qualify under that definition. Original maturity means original maturity to the entity holding the investment. For example, both a three-month US Treasury bill and a three-year Treasury note purchased three months from maturity qualify as cash equivalents.
Instead, it represents equity, which establishes an individual’s ownership in a company. A liability is an obligation consisting of an amount owed to another individual. A liability can also be money received in advance prior to its being earned. Profit it earns—that is, the growth or decline in its stock of assets from all sources other than contributions or withdrawals of funds by owners and creditors.
Components of the Balance Sheet and What They Can Tell Us
The shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet contains related amounts called additional paid-in capital and contributed capital. These represent Exxon’s long-term investments like oil rigs and production facilities that come under property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). Total noncurrent assets for fiscal-year end 2021 were $279.7 billion. Current assets generally sit at the top of the balance sheet.
However, a Treasury note purchased three years ago does not become a cash equivalent when its remaining maturity is three months. Also known as the « acid test » ratio, this is a refinement of the current ratio and is a more conservative measure of liquidity. The quick ratio expresses the degree to which a company’s current liabilities are covered by the most liquid current assets. Generally, any value of less than 1 to 1 implies a reciprocal dependency on inventory or other current assets to liquidate short-term debt. During the course of preparing your balance sheet you will notice other assets that cannot be classified as current assets, investments, plant assets, or intangible assets. These assets are listed on your balance sheet as other assets. There are two broad categories of assets, these are current assets and non-current assets.
Whatever system of classification is used should be applied on a consistent basis, so that balance sheet information is comparable over multiple reporting periods. Amount of investment in marketable security, classified as current. The value of a trust established to hold the stock of an employee compensation and benefits plan as of the balance sheet date. Intangible assets are not physical in form but offer significant company value. For example, if you have a loan on your equipment, it is a liability.
- Current assets are generally reported on the balance sheet at their current or market price.
- Noncurrent assetsare a company’slong-term investments that have a useful life of more than one year.
- Plus, you can protect the value if you decide to upgrade or sell later.
- Noncurrent assets are not depreciated in order to represent a new value or a replacement value but simply to allocate the cost of the asset over a period of time.
- This ratio measures a firm’s liquidity – whether it has enough resources to pay its current liabilities.
Net income is the accountant’s term for the amount of profit that is reported for a particular time period. Because the two sides of this balance sheet represent two different aspects of the same entity, the totals must always be identical. Thus, a change in the amount for one item must always be accompanied by an equal change in some other item. For example, if the company pays $40 to one of its trade creditors, the cash balance will go down by $40, and the balance in accounts payable will go down by the same amount. Sum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are expected to be realized in cash, sold, or consumed within one year .
Example of a Classified Balance Sheet
Dividends are a distribution of the assets and usually paid in cash. They are paid quarterly or yearly by some companies while other companies do not pay dividends at any time. One difference between common stock asset or liability is that common stock is not an asset nor a liability.
Is capital a current or noncurrent liabilities?
Companies use capital leases to finance the purchase of fixed assets, such as industrial equipment and motor vehicles. If the lease term exceeds one year, the lease payments made towards the capital lease are treated as non-current liabilities since they reduce the long-term obligations of the lease.
It is the profit a company gets when it issues the stock for the first time in the open market. Whether the classification Is contributed capital a noncurrent asset or a current asset? of common stock is considered current or long-term depends on the company’s intent and ability.
